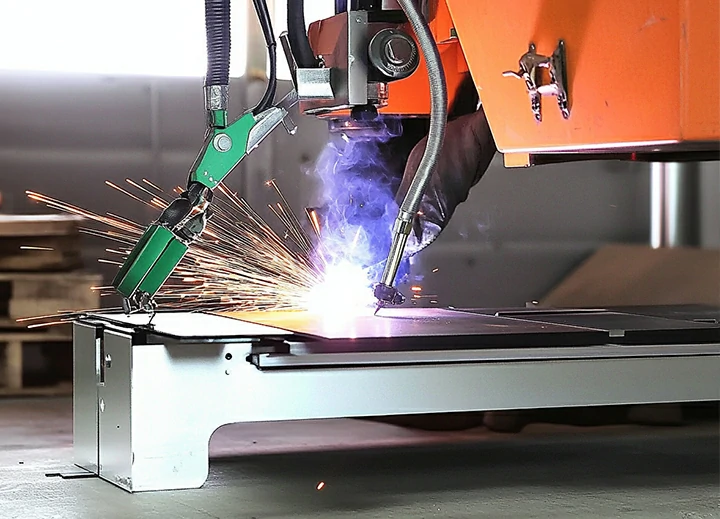
Our company specializes in advanced welding technologies, including Gas Tungsten Arc Welding (TIG), arc welding, and laser welding, to provide high-quality, durable, and precise welded components. With the most advanced equipment and a highly skilled team, we offer tailor-made welding solutions for industries such as construction, machinery, and marine.
Process Characteristics:
The equipment is simple, and the operation is flexible. It can be carried out in various positions and is adaptable to welded workpieces of different shapes and structures. However, its production efficiency is relatively low, and it demands a high level of skill from welders.
Applicable Materials:
It is widely applied to the welding of metallic materials such as carbon steel, low-alloy steel, and stainless steel. For instance, in fields like construction steel structures and machinery manufacturing, for some parts where automated welding is difficult to implement, manual arc welding is a commonly adopted welding method.
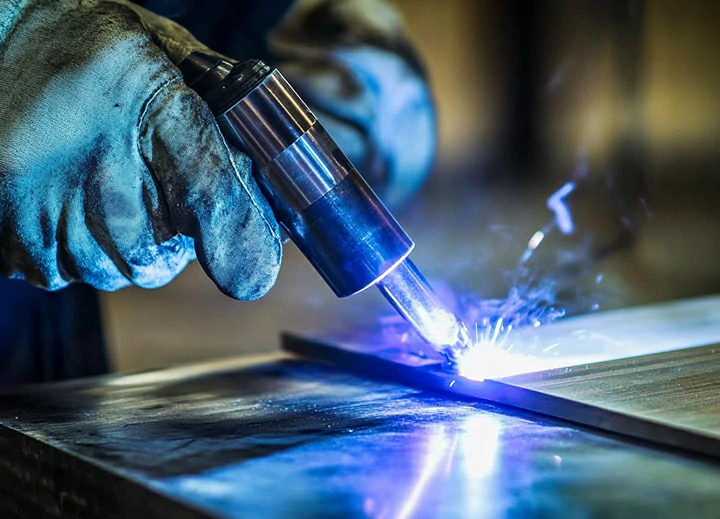

Process Characteristics:
It encompasses Tungsten Inert Gas Welding (TIG) and Metal Inert Gas Welding / Metal Active Gas Welding (MIG/MAG). Gas shielded welding boasts advantages such as high welding quality, stable arc, concentrated heat, and minimal deformation. Moreover, it enables automated welding, resulting in high production efficiency.
Applicable Materials:
TIG welding is frequently used for the welding of non-ferrous metals such as stainless steel, aluminum and its alloys, copper and its alloys. It is especially suitable for thin plate welding and root pass welding, like the welding of stainless steel kitchen utensils and aluminum alloy doors and windows. MIG/MAG welding is applicable to materials including carbon steel, low-alloy steel, stainless steel, aluminum and its alloys, and is widely used in industries such as automotive manufacturing and shipbuilding, which can be used for welding relatively thick plates.

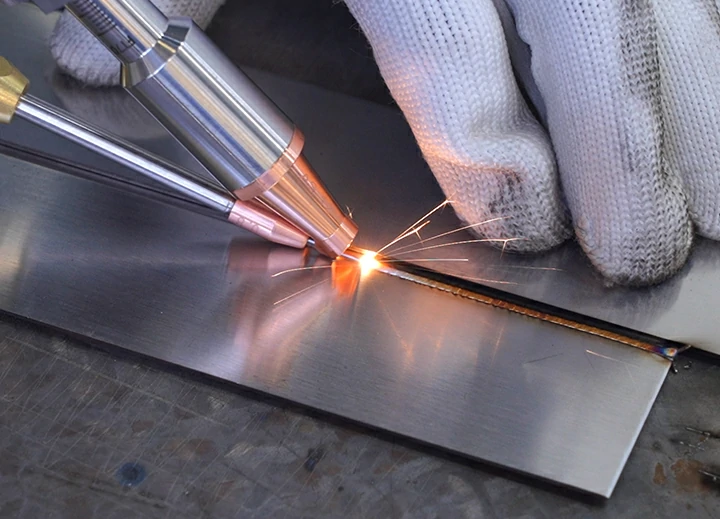
Process Characteristics:
Laser welding is a method that uses a laser beam with a high energy density as the heat source for welding. It has advantages such as high energy density, fast welding speed, narrow and deep weld seams, a small heat-affected zone, minimal welding deformation, and the ability to achieve precise welding. However, the equipment is expensive, and it has high requirements for the assembly accuracy of the welded workpieces.
Applicable Materials:
It is suitable for various metallic materials, especially widely applied in the welding of high-performance materials such as stainless steel, titanium alloys, aluminum alloys, and some precision parts. For example, it is used in the welding of titanium alloy structural parts in the aerospace field and the welding of micro components in the electronics industry.